首页
/
/
/
/
Hinokitiol/桧木醇
Hinokitiol/桧木醇
{[allProObj[0].p_purity_real_show]}
货号:A161005
同义名:
β-桧木醇
/ β-Thujaplicin; NSC 18804
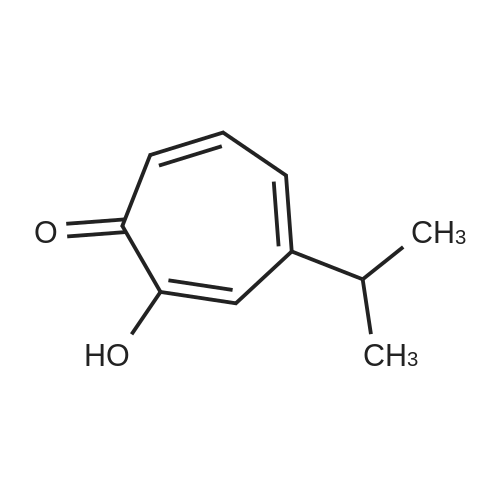
Hinokitiol 是一种天然存在的单萜酚,具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗炎和抗肿瘤活性,可调节铁代谢并通过降低 Nrf2 的表达影响 DNA 甲基化相关蛋白的表达。
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 化学结构
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 3D分子结构
规格
价格
会员价
库存
数量
{[ item.pr_size ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb, 1,1) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb_sale, 1,1) ]}
{[ suihuo_tips(item.pr_tag_price) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb, 1,1) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb,item.pr_rate,1) ]}
{[ suihuo_tips(item.pr_tag_price) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb, 1,1) ]}{[ suihuo_tips(item.pr_tag_price) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb_sale, 1,1) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb,item.pr_rate,item.mem_rate) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_rmb,1,item.mem_rate) ]}
现货
1周
咨询
-
+
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 纯度/质量文件 产品仅供科研
货号:A161005
标准纯度:
{[allProObj[0].p_purity_real_show]}
产品说明书
全球学术期刊中引用的产品
• Science , 2025, 387(6729): eadp5637. Ambeed. • Nat. Electron. , 2025, 8, 66-74. Ambeed. • Adv. Mater. , 2025, 2416621. Ambeed. • Adv. Mater. , 2025, 2410493. Ambeed. • Adv. Mater. , 2025, 2420319. Ambeed. A106129
]
更多 >
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 质控信息
CDC25B-IN-2
✔
Akt
99%+
Clevidipine
✔
97%
Verapamil HCl
✔
99%
Amlodipine
✔
99%
Amlodipine maleate
✔
98%
(+)-cis-Diltiazem HCl
✔
99%
Zegocractin
++
Orai1/STIM1-mediated Ca2+ currents, IC50: 120 nM
99%+
Tanshinone IIA sulfonate sodium
✔
98%
Ulixacaltamide
++
hCaV3.1, IC50: 50 nM
hCaV3.2, IC50: 110 nM
99%+
Dronedarone HCl
✔
95%
Nitrendipine
+
Calcium channel, IC50: 95 nM
98%
Efonidipine HCl monoethanolate
✔
98%
Cinnarizine
✔
98%
SEA0400
++
ROS,p38 MAPK,ERK
99%+
Fasudil HCl
✔
Rho,PKA
98%
ML-9
✔
Akt,MLCK
99%+
Flunarizine 2HCl
+
Calcium channel, Ki: 68 nM
95%
Lomerizine 2HCl
✔
98%
Efonidipine
✔
98%
Levamlodipine
✔
98%
Nisoldipine
++
L-type Cav1.2, IC50: 10 nM
97%
Isradipine
✔
98%
Lacidipine
✔
98%
Lercanidipine
✔
99%
Loureirin B
✔
Potassium Channel
99%+
Tetracaine HCl
✔
98%
Manidipine
+++
Calcium channel, IC50: 2.6 nM
99%
Manidipine Dihydrochlorid
+++
Calcium channel, IC50: 2.6 nM
98%
Nicardipine
✔
99%
Wilforgine
✔
98+%
Econazole
✔
99%+
Ginsenoside Rd
✔
NF-κB
98%
Fendiline HCl
✔
98+%
Mesaconitine
✔
98%
Tetrandrine
✔
95%
Nifedipine
✔
98%
Nilvadipine
++++
Calcium channel, IC50: 0.03 nM
95%
Barnidipine
++++
[3 H]nitrendipine, Ki: 0.21 nM
95+%
Azelnidipine
✔
97%
Levetiracetam
✔
98%
Nimodipine
✔
95%
Benidipine HCl
✔
98%
Pinaverium bromide
✔
98%
Pranidipine
✔
99%
NP118809
+
L-type calcium channel, IC50: 12.2 μM
N-type Ca2+ channel, IC50: 0.11 μM
98%
Amlodipine Besylate
+++
Calcium channel, IC50: 1.9 nM
97%
Cilnidipine
✔
99%
Cinepazide Maleate
✔
99% (HPLC)
Terfenadine
✔
98%
YM-58483
✔
99%+
Amiloride HCl
✔
98%
Ranolazine
✔
98%
Praeruptorin A
✔
Akt,p38 MAPK
98%
Ranolazine 2HCl
✔
98%
Felodipine
++++
L-type calcium channel, IC50: 0.15 nM
98%
PD173212
+++
N-type Ca2+ channel, IC50: 36 nM
98%
Levamlodipine besylate
✔
97%
Carboxyamidotriazole Orotate
✔
98%
IGS-1.76
✔
98+%
WH-4-023
++++
++++
99%+
展开
1. 鼠标悬停在“+”上可以显示相关IC50的具体数值。"+"越多,抑制作用越强。2. "✔"表示该化合物对相应的亚型有抑制作用,但抑制强度暂时没有相关数据。
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 生物活性
描述
Hinokitiol, a tropolone-related natural compound, is known to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and has anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activities. Hinokitiol may exert DNA demethylation by inhibiting the expression of DNMT1 (DNA methyltransferase 1) and UHRF1 (RING finger domain 1) in colon cancer cells[3] [4] [5] [6]
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 参考文献
[1] Lee JH, Moon JH, et al. SIRT1, a Class III histone deacetylase, regulates LPS-induced inflammation in human keratinocytes and mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of hinokitiol. J Invest Dermatol. 2017 Feb 28. pii: S0022-202X(17)31149-1.
[2] Seo JS, Choi YH, et al. Hinokitiol induces DNA demethylation via DNMT1 and UHRF1 inhibition in colon cancer cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2017 Feb 27;18(1):14.
[3] Seo JS, Choi YH, Moon JW, Kim HS, Park SH. Hinokitiol induces DNA demethylation via DNMT1 and UHRF1 inhibition in colon cancer cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2017;18(1):14.
[4] Ouyang WC, Liao YW, Chen PN, Lu KH, Yu CC, Hsieh PL. Hinokitiol suppresses cancer stemness and oncogenicity in glioma stem cells by Nrf2 regulation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017;80(2):411‐419
[5] Lu WJ, Lin KH, Tseng MF, et al. New therapeutic strategy of hinokitiol in haemorrhagic shock-induced liver injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(3):1723‐1734
[6] Jayakumar T, Liu CH, Wu GY, et al. Hinokitiol Inhibits Migration of A549 Lung Cancer Cells via Suppression of MMPs and Induction of Antioxidant Enzymes and Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):939.
展开
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 实验方案
计算器
摩尔计算器
总药量计算器
工作液计算器
存储液制备
1mg
5mg
10mg
1 mM
5 mM
10 mM
6.09mL
1.22mL
0.61mL
30.45mL
6.09mL
3.05mL
60.90mL
12.18mL
6.09mL
Hinokitiol/桧木醇 技术信息