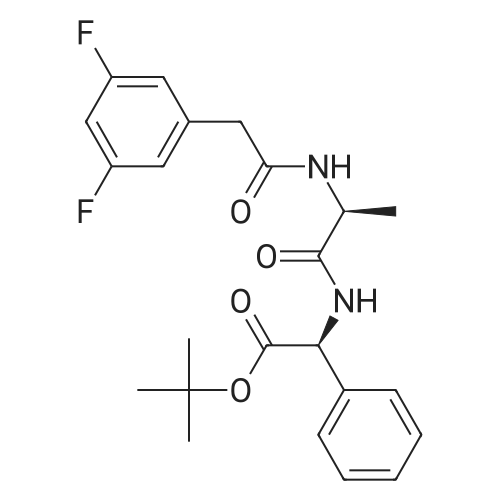
Ambeed 大中华区
CN | ZH
-
产品中心
- 按产品类型
- Inhibitors/Agonists | 抑制剂/激动剂
- Inhibitory Monoclonal Antibody | 单抗抑制剂
- Animal Modeling Reagent | 动物造模剂
- Antibiotic and Antivirus | 抗生素和抗病毒
- Biochemical reagent | 生化试剂
- Cell Biology | 细胞生物学
- Compound Libraries | 化合物库
- Endocrine and metabolic diseases | 内分泌与代谢疾病
- Enzymology | 酶学
- Fluorescent Probe / Staining | 荧光探针/染色
- Molecular Biology | 分子生物学
- Natural product | 天然产物
- Pharmaceutical Research | 药物研究
- PROTAC | 蛋白降解靶向嵌合体
- Recombinant Proteins | 重组蛋白
- Zoology and Botany | 动物学与植物学
-
抑制剂/激动剂
- 抑制剂/激动剂
- Angiogenesis | 血管生成
- Anti-infection | 抗感染
- Antibody-drug Conjugate/ADC Related | 抗体-药物偶联物
- Apoptosis | 细胞凋亡
- Autophagy | 自噬
- Cell Cycle | 细胞周期
- Cell Death | 细胞死亡
- Cytoskeleton | 细胞骨架
- DNA Damage | DNA损伤
- Endocrinology/Hormones | 内分泌学/激素
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress | 内质网应激
- Epigenetics | 表观遗传学
- Ferroptosis | 铁死亡
- GPCR/G Protein | G蛋白偶联受体/G蛋白
- Hedgehog (Hh)
- Hippo
- Immunology/Inflammation | 免疫/炎症
- JAK-STAT-Signaling
- MAPK/ERK Pathway
- Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel | 膜转运蛋白
- Metabolic Enzyme | 代谢酶
- Neuronal Signaling | 神经信号通路
- NF-κB
- Notch Signaling Pathway
- Obesity and Diabetes | 肥胖与糖尿病
- Other Inhibitors/Agonists | 其他抑制剂/激动剂
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- PPAR Signaling Pathway
- Protease | 蛋白酶
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK | 蛋白质酪氨酸激酶
- Pyroptosis | 细胞焦亡
- Stem Cells | 干细胞
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Toll-like Receptor (TLR) | Toll样受体
- Ubiquitin | 泛素
- Vitamin D related/nuclear receptor | 维生素D相关/核受体
- Wnt Signaling Pathway