| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
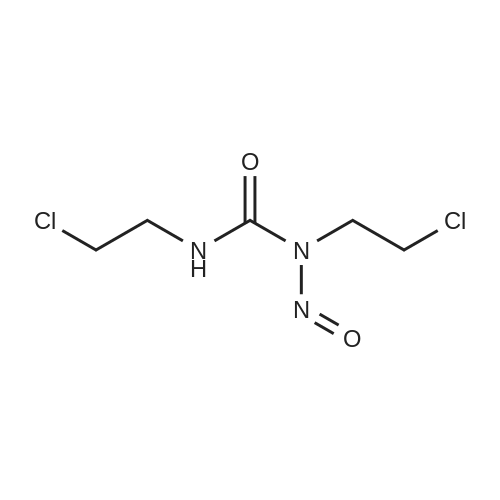
| 描述 | Carmustine is an antitumor chemotherapeutic agent, which works by akylating DNA and RNA. NAT (N-acetyltransferase) activity in glial tumor cell cytosols and intact tumor cells were decreased by carmustine in a dose-dependent manner. Carmustine (8, 80, and 800 µM) decreases N-acetyltransferase (NAT) activities for 2-aminofluorene (AF) and p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) in rat glial tumor cytosol and intact cells. In rat glial tumor cells, the DNA-AF adduct increases, and carmustine decreases the formation of DNA-AF adduct[3]. Preincubation of cells with the glutathione reductase inhibitor, carmustine, led to elevated basal [Ca2+]i, yet the cells remained responsive to bradykinin[4]. Carmustine (≥25 µM) stimulates eryptosis at least partially by increasing cytosolic Ca²⁺ activity[5]. Carmustine (BCNU; 25 mg/kg, i.p.) causes higher levels of the rhe ratio of liver weight to body weight and plasma conjugated bilirubin, and lower biliary flow, oxidised glutation levels (GSSG) and reduced glutation (GSH)/GSSG values compared with control rats[6]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
4.67mL 0.93mL 0.47mL |
23.36mL 4.67mL 2.34mL |
46.72mL 9.34mL 4.67mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|