| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
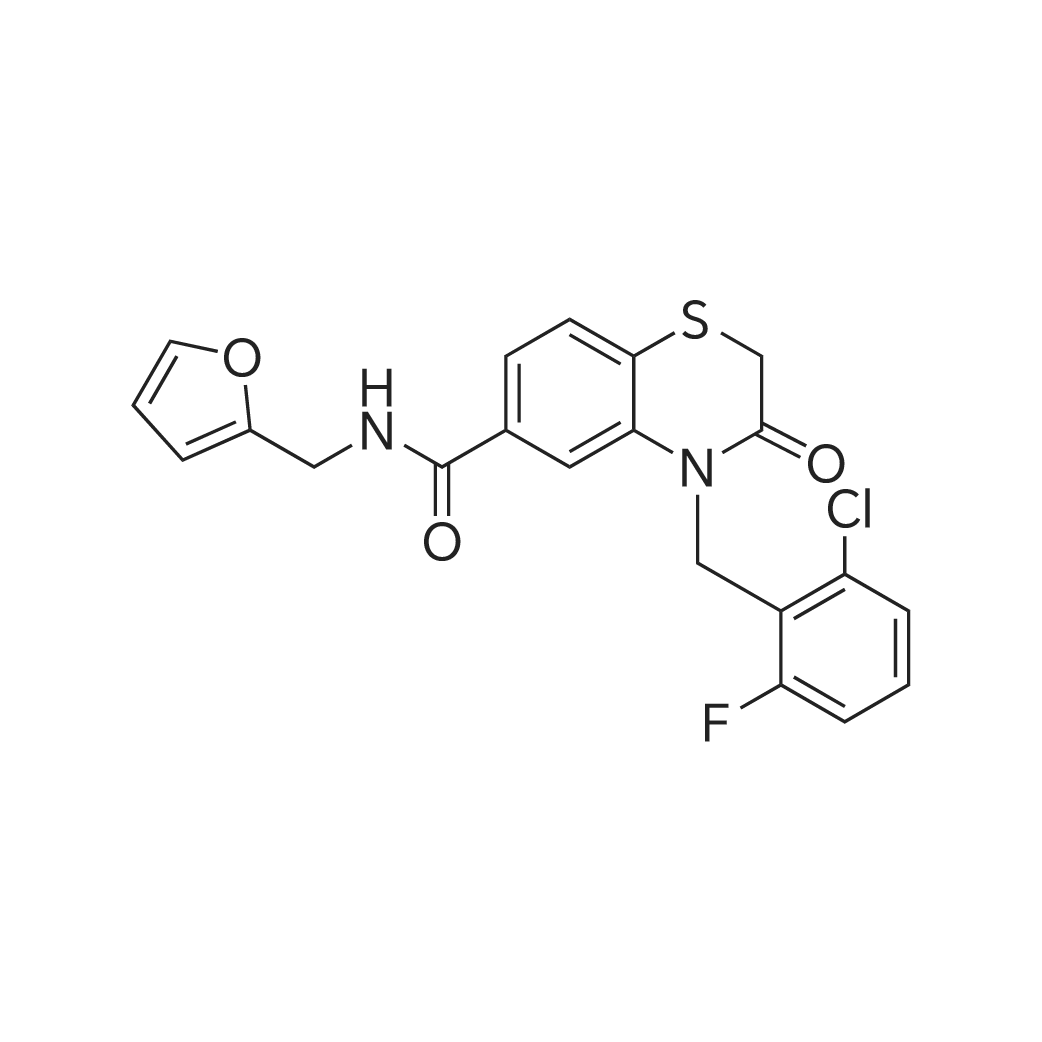
| 描述 | STING is a pattern recognition receptor of cyclic dinucleotides and an innate immune adaptor protein. STING agonist-1 is a human-specific STING agonist with antiviral activity. It inhibited replication of Chikungunya Virus and Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus with IC90 values 8.01μM of 24.57μM, respectively. Exposing human fibroblasts to STING agonist-1 (100μM) led to transcription of cellular genes triggered by IRF3/IFN-dependent signaling, but not NF-κB-dependent signaling. STING agonist-1 at a concentration of 100μM also induced IRF3 phosphorylation and elicited anti-alphaviral activity in cells lacking IPS1. In human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, treatment with STING agonist-1 (25–100μM) for 8 hours induced innate antiviral mRNA expression, including IFIT1, IFIT2, IFNβ, ISG15, OAS, and Viperin[2]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.32mL 0.46mL 0.23mL |
11.60mL 2.32mL 1.16mL |
23.21mL 4.64mL 2.32mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|