| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
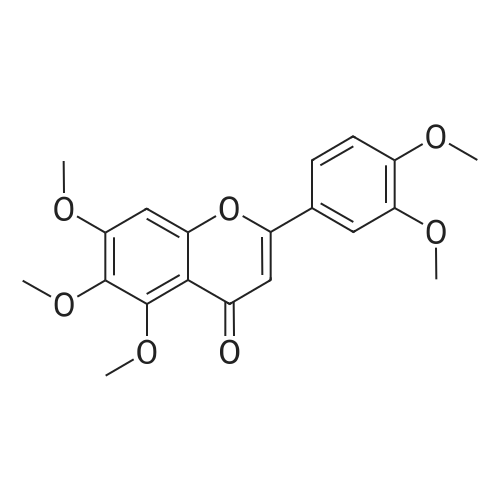
| 描述 | Sinensetin is a methylated flavone found in certain citrus fruits. Sinensetin enhances adipogenesis and lipolysis by increasing cAMP levels in adipocytes[3]. Sin (Sinensetin) may inhibit chondrocyte apoptosis induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP); at the same time, it might also inhibit the production of MMP13 and promote the production of aggrecan and collagen II. Sin promotes chondrocyte autophagy by activating AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway[4]. SIN significantly induced cell death in HepG2 cells, whereas the proliferation rate of Thle2, human liver epithelial cells, was unaffected by SIN[5]. Sinensetin has potential capacity to attenuate IAV (influenza A virus)-triggered pro-inflammatory response via inactivation of NF-κB, ERK1/2 MAPK and p38 MAPK signalings[6]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.69mL 0.54mL 0.27mL |
13.43mL 2.69mL 1.34mL |
26.86mL 5.37mL 2.69mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|