| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
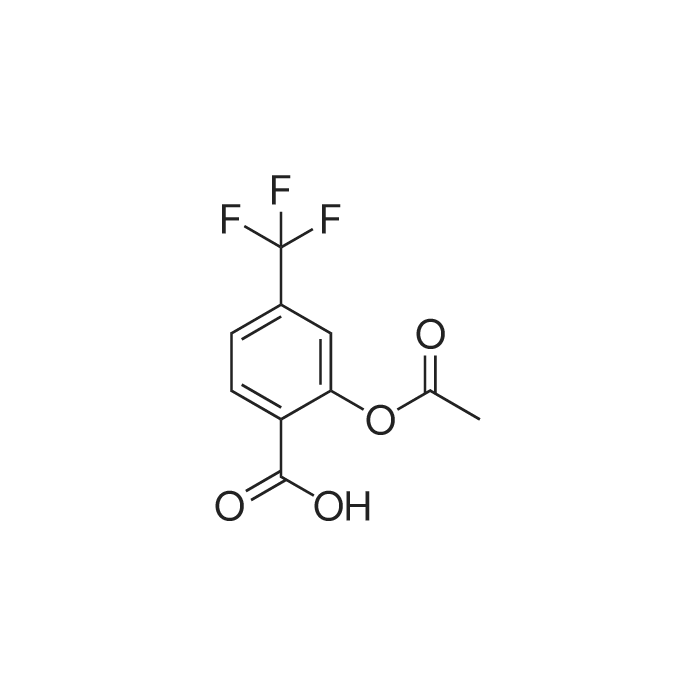
| 描述 | Triflusal is a derivative of salicylic acid with a well-established platelet aggregation inhibitory profile. Triflusal is a potentially useful choice in the treatment and prophylaxis of brain ischemia[3]. Triflusal inhibited COX-2-mediated prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production (IC50 = 0.16). Triflusal (but neither aspirin nor salicylate) produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of COX-2 protein expression in peripheral human mononuclear cells. In a rat air pouch model in vivo, in which both aspirin and triflusal inhibited PGE2 production (ID50 = 18.9 and 11.4 mg/kg p.o., respectively) but only triflusal-treated animals showed a decrease in COX-2 expression[4]. Triflusal (10 mg/kg i.v.) reduces platelet deposition on subendothelium-induced primary thrombus by about 68% in rabbits. Triflusal (10 mg/kg i.v.) reduces platelet deposition on a fresh thrombus formed over tunica media by about 48% in rabbits. Triflusal (40 mg/kg p.o.) reduces platelet deposition on a primary thrombus triggered by subendothelium and tunica media by 53% in rabbits. Triflusal (40 mg/kg p.o.) significantly reduces COX-2 mRNA levels and protein levels without influence COX-1 mRNA levels on the vascular wall in rabbits[5]. Triflusal (600 mg/day for 5 days) results in an increase in NO production by neutrophils and an increase in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) protein expression in neutrophils in healthy volunteers[6]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
4.03mL 0.81mL 0.40mL |
20.15mL 4.03mL 2.01mL |
40.30mL 8.06mL 4.03mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|