| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
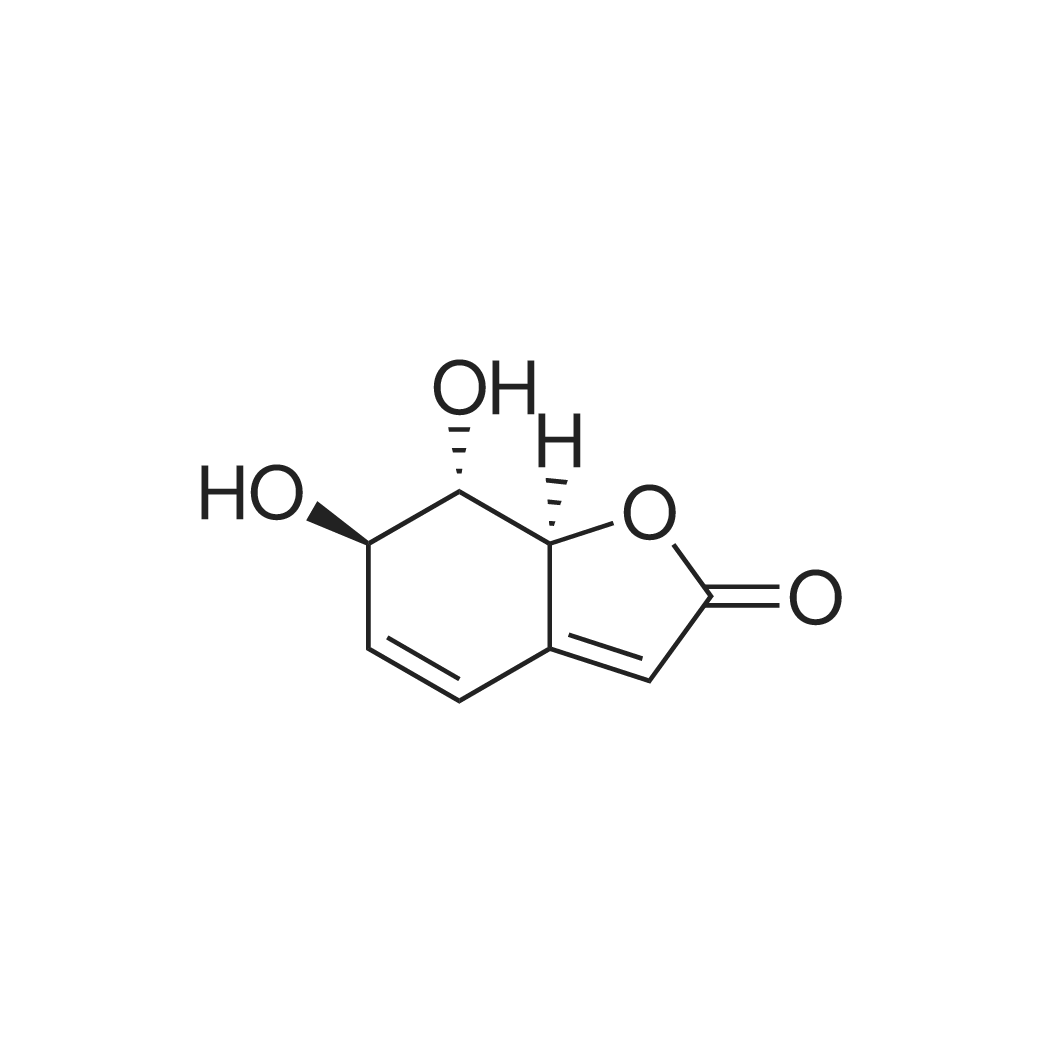
| 描述 | Griffonilide is a butenolide, isolated from the roots of Semiaquilegia adoxoides, and often occurs alongside lithospermoside[3]. Morama beans are a rich source of phenolic acids, flavonoids, certain fatty acids, non-essential amino acids, certain phytosterols, tannins and minerals. The plant's tuber contains griffonilide, behenic acid and starch. Concoctions of extracts from morama bean, tuber and other local plants are frequently used to treat diarrhoea and digestive disorders by the San and other indigenous populations[4]. The investigation of Tylosema esculentum (Morama) husks, cotyledons, and tuber yielded griffonilide 2, compound 1, griffonin 3, gallic acid 4, protocatechuic acid 5, β-sitosterol 6, behenic acid 7, oleic acid 8, sucrose 9, 2-O-ethyl-α-D-glucopyranoside 10, kaempferol 11 and kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside 12. The tuber extracts were inactive against Caco-2 and Hela cell lines, while the husk extracts showed low activity against Caco-2 and Vero cell line with IC(50) values >400 μg/mL. The GC-MS analysis showed the beans and tuber non-polar (n-hexane) extracts major constituents as fatty acids[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
5.95mL 1.19mL 0.59mL |
29.74mL 5.95mL 2.97mL |
59.47mL 11.89mL 5.95mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|
|
[2]Giurleo, Daniel, et al. A phytochemical exploration of Griffonia simplicifolia seeds and leaves. |