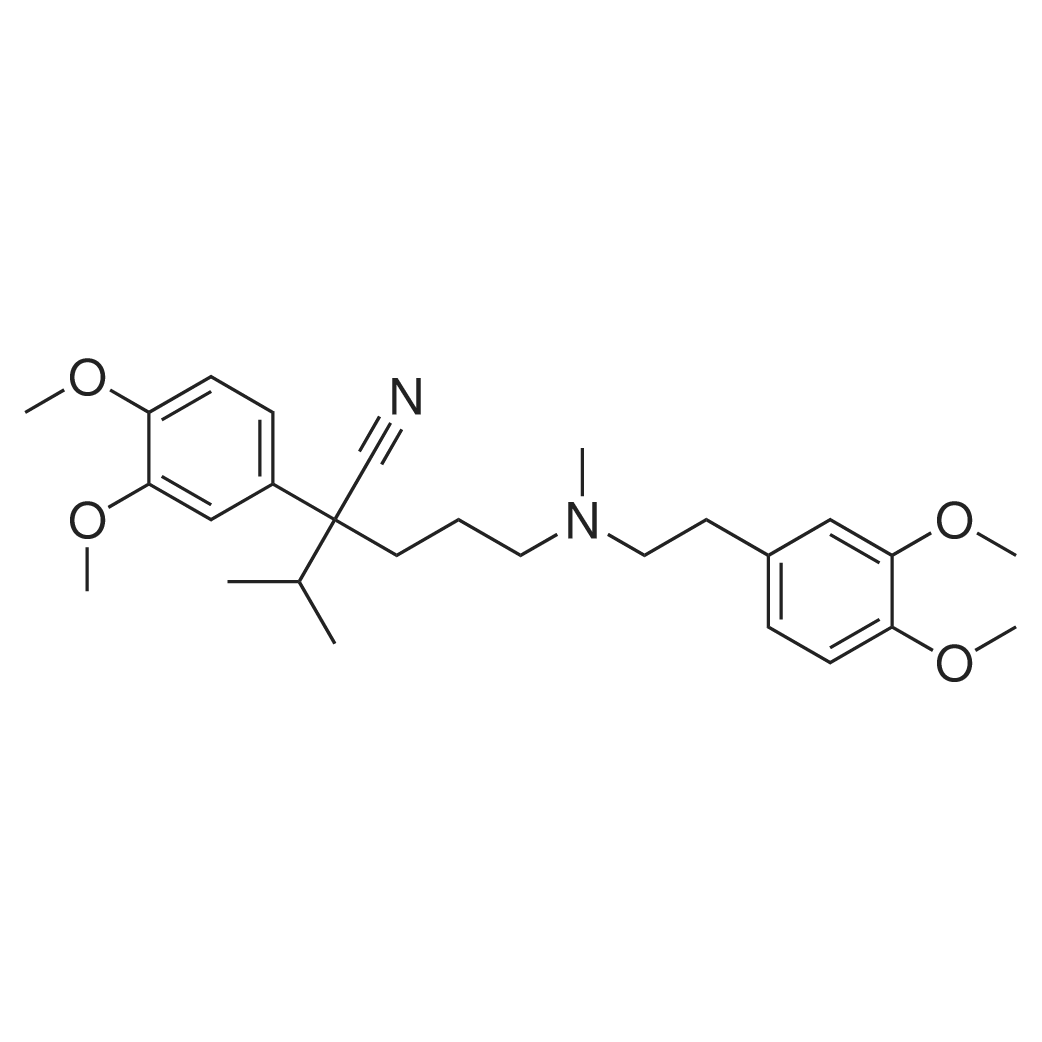
| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 描述 | Verapamil is a calcium channel blocker. Intravenous verapamil is highly effective in the termination of paroxysmal reciprocating atrioventricular tachycardia, whether associated with preexcitation or involving the atrioventricular node alone. Given orally it is useful for the prophylaxis of atrioventricular reentry tachycardia, and also in modulating the atrioventricular nodal response in atrial fibrillation[4]. The EverFluor FL Verapamil (EFV) uptake by TR-iBRB2 cells is inhibited by cationic drugs, and inhibits by verapamil in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 98.0 μM[5]. Approximately 80 percent of patients with PSVT will convert to normal sinus rhythm after verapamil 0.075-0.15 mg/kg. Atrial fibrillation and flutter seldom convert to sinus rhythm with verapamil, but it successfully reduces the ventricular rate in 90 percent of these patients. Verapamil is useful for the rapid conversion of PSVT to normal sinus rhythm and for the rapid control of ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and flutter before other antiarrhythmics have taken effect[6]. Verapamil (1 mg/kg) significantly decreases the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias including premature ventricular contractions (PVC), ventricular tachycardia (VT) and ventricular fibrillation (VF) for 45-min coronary artery occlusion. Verapamil (1 mg/kg) significantly decreases the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias including premature ventricular contractions (PVC), ventricular tachycardia (VT) and ventricular fibrillation (VF) for 45-min coronary artery occlusion[7]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.20mL 0.44mL 0.22mL |
11.00mL 2.20mL 1.10mL |
22.00mL 4.40mL 2.20mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|
|
[4]Krikler DM. Verapamil in arrhythmia. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;21 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):183S-189S |