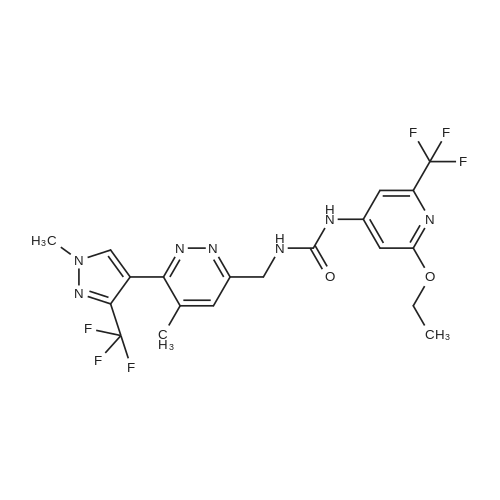
| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 描述 | Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), a metabolic product of cell membrane sphingolipids, is bound to extracellular chaperones, is enriched in circulatory fluids, and binds to G protein-coupled S1P receptors (S1PRs) to regulate embryonic development, postnatal organ function, and disease. S1PRs regulate essential processes such as adaptive immune cell trafficking, vascular development, and homeostasis. Moreover, S1PR signaling is a driver of multiple diseases[1]. S1P regulates cell fate, vascular tone, endothelial function and integrity as well as lymphocyte trafficking, thus disbalance in its production and signaling has been linked with development of such pathologies as arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction and aberrant angiogenesis. Number of signaling mechanisms are critical - from endothelial nitric oxide synthase through STAT3, MAPK and Akt pathways to HDL particles involved in redox and inflammatory balance[2]. In vivo, HDL-S1P injection significantly reduced pulmonary oedema and endothelial leakage in septic rats. In vitro, cell experiments showed that HDL-S1P effectively protected the proliferation and migration abilities of endothelial cells, which could be partly explained by its biased activation of the S1P receptor 1[3]. GLPG2938 is an antagonists of S1P receptor for prophylaxis and/or treatment of diseases including fibrotic, inflammatory, autoimmune, metabolic, cardiovascular, and/or proliferative diseases. GLPG2938 displayed S1P inhibitory activity with EC50 value of 9.5 nM (S1P2 antagonist EC50)[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.99mL 0.40mL 0.20mL |
9.93mL 1.99mL 0.99mL |
19.86mL 3.97mL 1.99mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|