| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
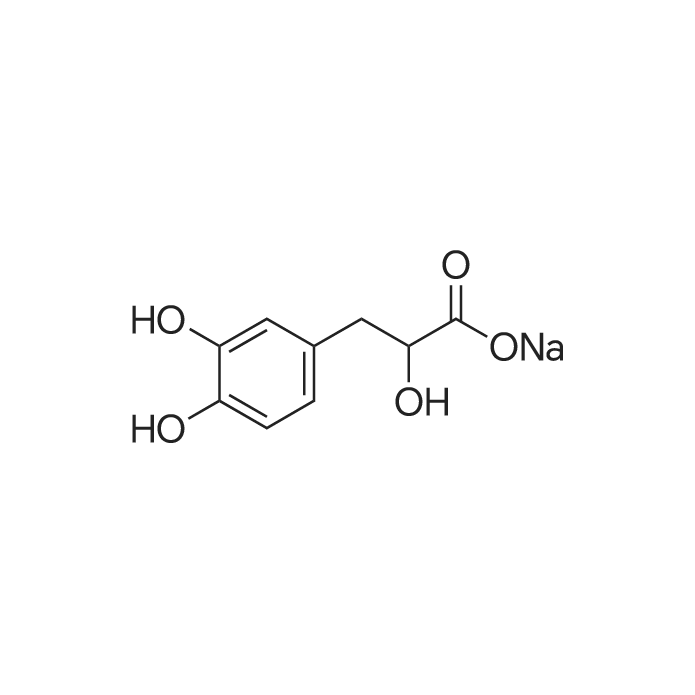
| 描述 | Sodium Danshensu is odium salt of danshensu from the widely used Chinese herb Danshen. In thoracic arteries under basal tonus, sodium danshensu (0.3-3 g/L) produced a dose-dependent transient contraction. In phenylephrine-precontracted thoracic arteries with or without endothelium, low concentration (0.1-0.3 g/L) of sodium danshensu produced a weak contraction, while high concentrations (1-3 g/L) produced a pronounced vasodilator after a transient vasocontraction. Pre-incubation with sodium danshensu could inhibit vessel contraction induced by phenylephrine and potassium chloride in a concentration-dependent way. Sodium danshensu inhibited phenylephrine- and CaCl(2)-induced vasoconstriction in Ca(2+)-free medium[3]. Sodium danshensu (SDS, 700 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) 10 min after stroke and once daily until animals were sacrificed. At 14 days after stroke, SDS significantly increased the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in the peri-infarct region. SDS-treated animals showed increased number of doublecortin (DCX)-positive cells[4]. Treatment with SDSS (Sodium Danshensu) for 5 days after MCAO (middle cerebral artery occlusion) remarkably improved neurologic deficits and survival rate, reduced infarct volume and the number of dead neurons. SDSS also decreased the number of apoptotic cells, regulated the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax, and increased the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
4.54mL 0.91mL 0.45mL |
22.71mL 4.54mL 2.27mL |
45.42mL 9.08mL 4.54mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|