| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
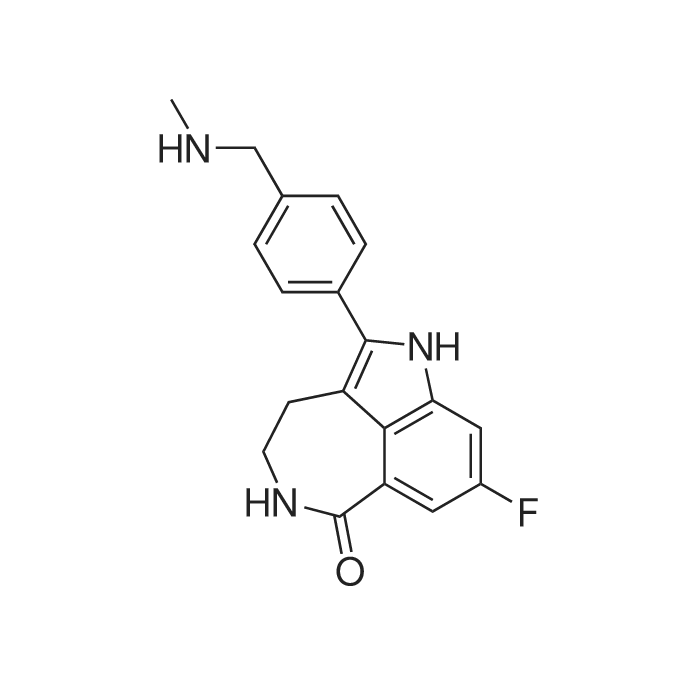
| 描述 | PARP1, also called as Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, is involved in the signaling of DNA damage. It can recognize and bind DNA single or double-strand breaks, thus possessing various cellular function, including regulation of apoptosis and chromosome stability, gene amplification and transcription, as well as cell division and differentiation. Rucaparib is a potent PARP inhibitor with Ki value of 1.4nM (measured by enzyme assays). Rucaparib at dose ranging in 1-10μM can suppress the level of PAR, as well as induce γ-H2AX, formation and PARP cleavage in a dose-dependent manner indicative of DNA damage and apoptosis, respectively, in MDA-MB468, MDA-MB-231, and Cal-51 cells in the presence of 5% FBS-supplemented DMEM medium for 72h. Rucaparib at concentrations>2.5μM decreased the p-Stat3 in MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231, as well as dose-dependently increased the p-Akt-S473 in MDA-MB-468 and Cal-51 cells. Rucaparib can chemosensitize neuroblastoma cell lines to temozolomide or topotecan in vitro and in vivo. Rucaparib at concentration of 0.4μM caused a significant sensitization of topotecan (1-30nM) and temozolomide (1-200μM) in NB-1691, SH-SY-5Y and SKNBE(2c) cells. Rucaparib (1mg/kg) increased the temozolomide-induced (68mg/kg) tumor growth delay by 50% (to >89 days) and complete and increased the number of mice with complete and persistent tumor regressions (≥100 days). Co-administration of Rucaparib (1mg/kg) with topotecan (1mg/kg) increased total number of complete regressions. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.09mL 0.62mL 0.31mL |
15.46mL 3.09mL 1.55mL |
30.93mL 6.19mL 3.09mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|