| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
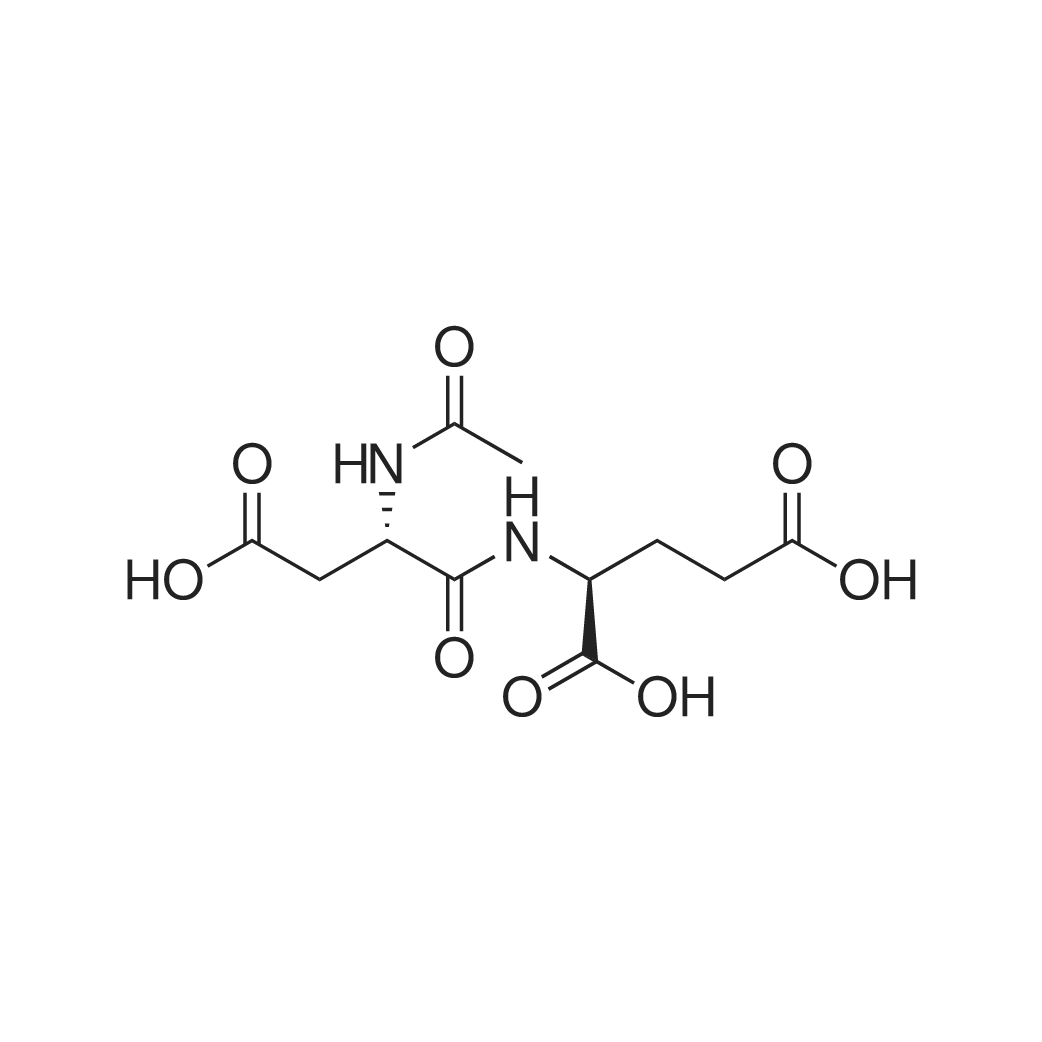
| 描述 | Spaglumic Acid (N-Acetylaspartylglutamic acid, NAAG) is a neuropeptide found in millimolar concentrations in brain that is localized to subpopulations of glutamatergic, cholinergic, GABAergic, and noradrenergic neuronal systems. NAAG is released upon depolarization by a Ca(2+)-dependent process and is an agonist at mGluR3 receptors and an antagonist at NMDA receptors[1]. EB (Evans blue) ocular extravasation was significantly lower in the eyes treated by spaglumic acid and emedastine. Spaglumic acid and emedastine seem to be the most useful drugs to reduce EB extravasation and allergic signs in an animal model of early phase allergic conjunctivitis[2]. The organ function decrease may be attributed by transcription alteration, inflammation response, and metabolic alteration in liver after BD. Spaglumic acid and halcinonide may be potential drugs for preventing organ damage during the BD (brain death) process[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.29mL 0.66mL 0.33mL |
16.43mL 3.29mL 1.64mL |
32.87mL 6.57mL 3.29mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|