| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
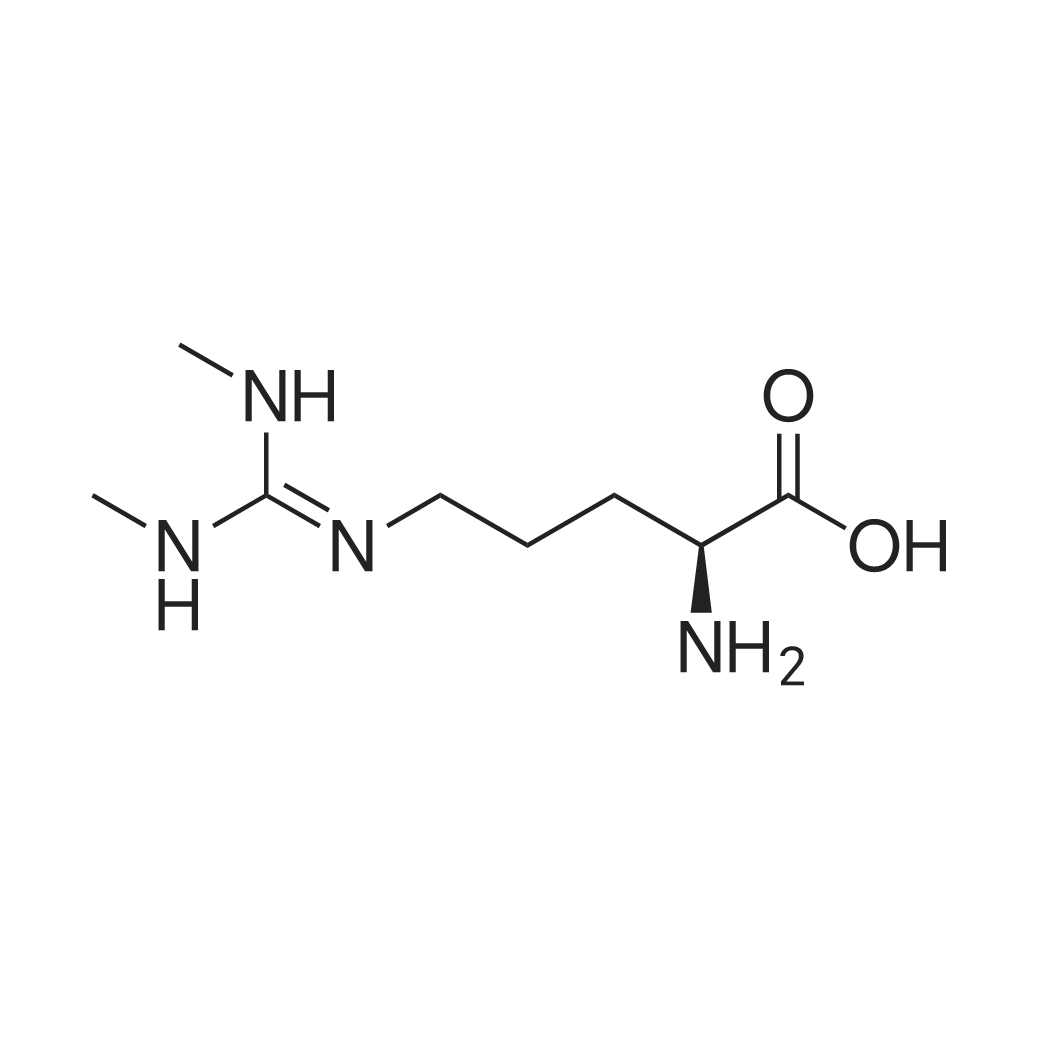
| 描述 | SDMA (Symmetric dimethylarginine) is an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide (NO) synthase activity. SDMA does not directly inhibit NOS but is a competitor of arginine transport. SDMA is primarily eliminated by renal excretion and is a promising endogenous marker of glomerular filtration rate. SDMA inhibited dose dependently the NO synthesis in intact endothelial cells, whereas it had no effect on protein expression of NOS[1]. SDMA is involved in the inflammatory process of chronic kidney disease, activating NF-κB and resulting in enhanced expression of IL-6 and TNF-α[2]. Chronic SDMA infusion leads to a significant increase of SDMA levels in mice, but the GFR (glomerular filtration rate) did not change at 4 weeks. No histological changes are observed, particularly no effect on fibrosis or endothelias nitric oxide synthase expression. There is neither an effect of SDMA on systolic blood pressure nor on ejection fraction[4]. SDMA is highly stable in serum and plasma, and the assay demonstrates excellent analytical performance. In unaffected dogs, SDMA remains unchanged whereas in affected dogs, SDMA increases during disease progression, correlating strongly with an increase in sCr and decrease in GFR[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
4.94mL 0.99mL 0.49mL |
24.72mL 4.94mL 2.47mL |
49.44mL 9.89mL 4.94mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|