| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
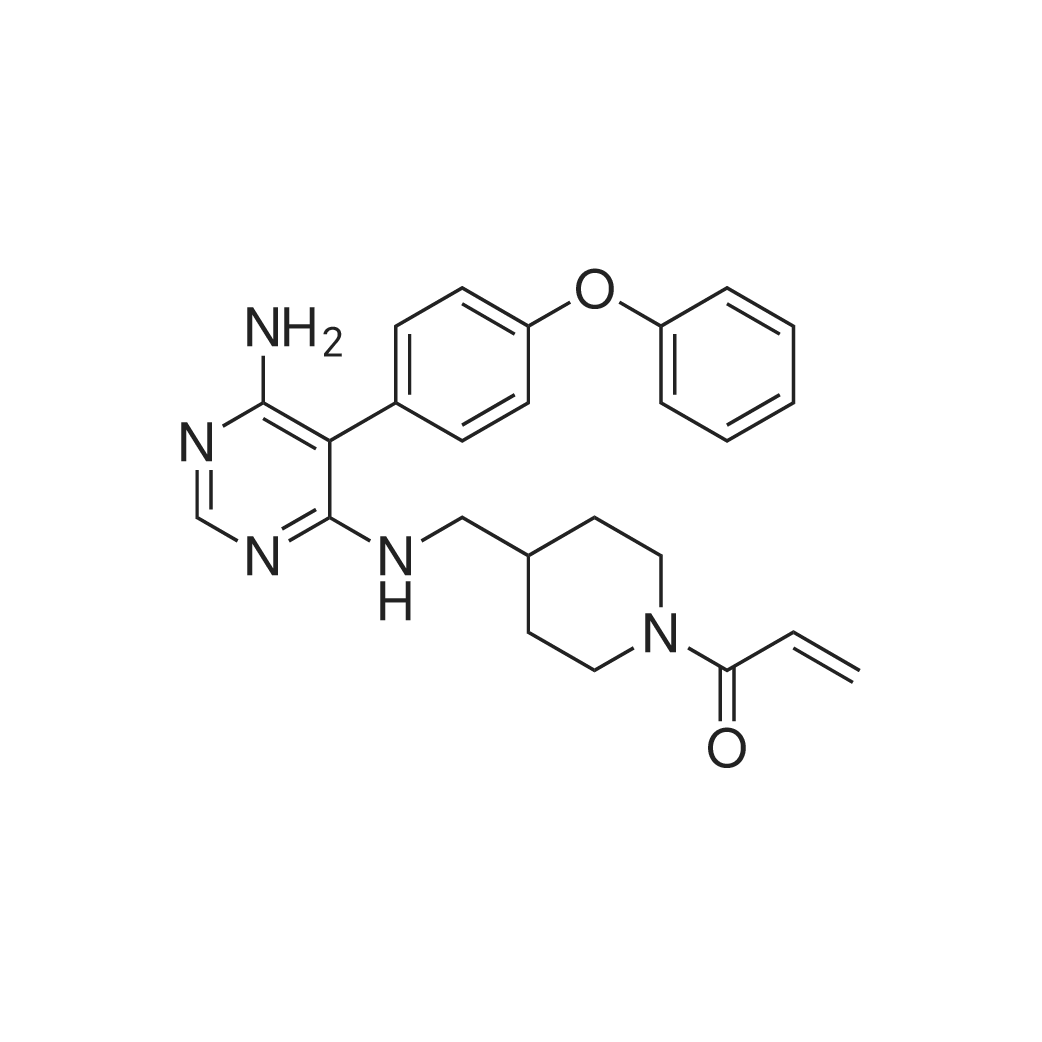
| 描述 | Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), a member of the Tec family of tyrosine kinases and expressed in B cells, macrophages, and monocytes but not in T cells, plays a crucial role in signaling through the B cell receptor (BCR) and the Fcγ receptor (FcγR) in B cells and myeloid cells, respectively. Evobrutinib, used for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, is a potent and irreversibly covalent BTK inhibitor with an IC50 of 8.9 nM. In a B cell stimulation assay in normal C57BL/6 mice, evobrutinib (1 mg/kg orally) achieved a B cell inhibition of 71% and 25% at 1 and 24 h. Evaluation of evobrutinib PK in mice, rats, and dogs indicated that evobrutinib is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with Cmax reached between 0.25 and 1 h. In a rat collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model, disease-induced ankle-swelling was significantly reduced (P≤0.05) for rats treated with evobrutinib 3 mg/kg (days 11−17), 10 mg/kg (days 11−17), 30 mg/kg (days 10−17), or methotrexate (days 11−17), compared with vehicle. Ankle histopathology scores were also reduced with evobrutinib in a dose-dependent manner compared to vehicle and the IC50 for evobrutinib was 5.180 mg/kg[3]. | ||
| 作用机制 | Evobrutinib covalently binds to Cys481 of the BTK kinase domain. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.33mL 0.47mL 0.23mL |
11.64mL 2.33mL 1.16mL |
23.28mL 4.66mL 2.33mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|