| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
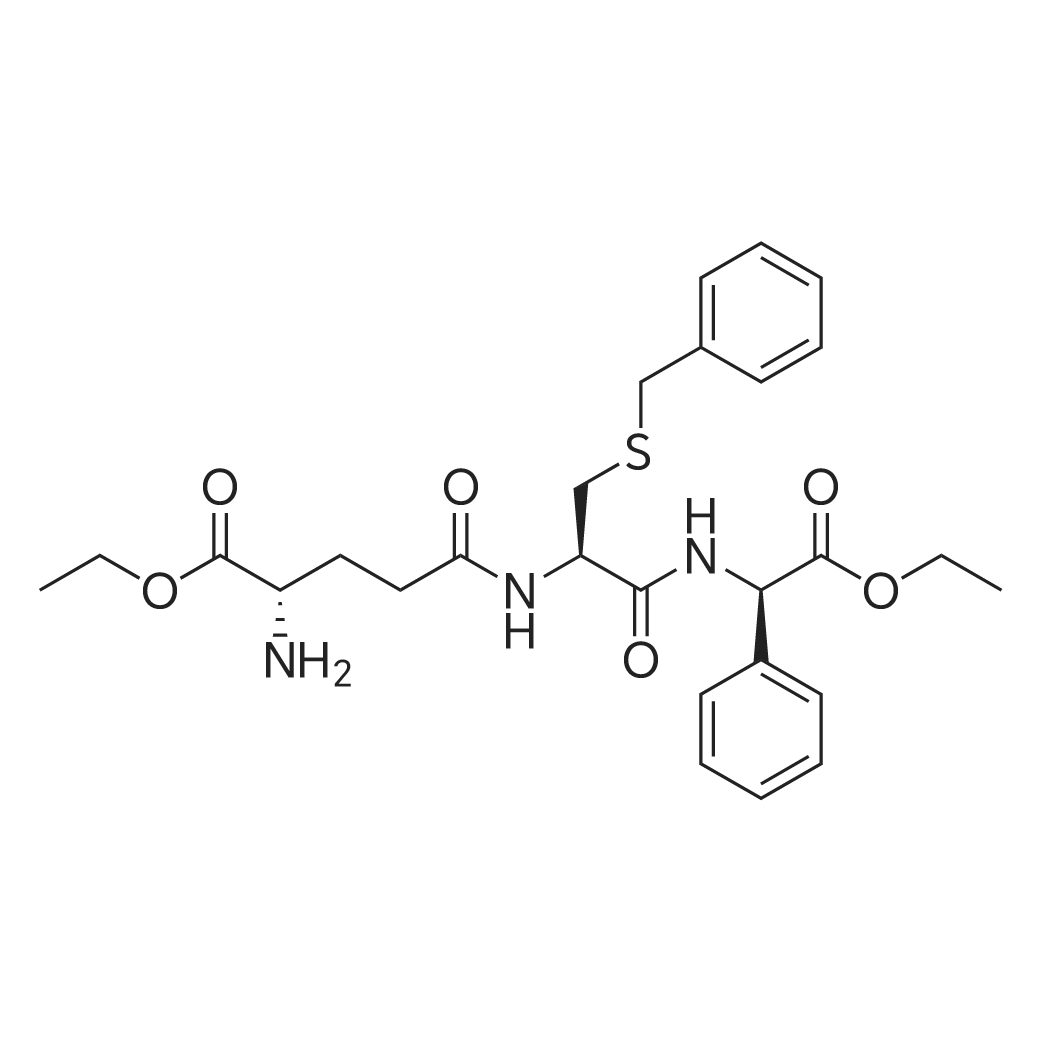
| 描述 | Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a clonal stem cell disorder resulting in bone marrow failure and variable cytopenias. While Glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTpi) contributes to the regulation of cell proliferation. Ezatiostat, a tripeptide analog of glutathione, is a selective and orally active inhibitor of GSTP1-1 having the potential for MDS treatment. Ezatiostat causes dissociation of GSTP1-1 from the jun-N-terminal kinase/c-Jun (JNK/JUN) complex, leading to JNK activation by phosphorylation. Activated JNK phosphorylates c-JUN, which ultimately results in the stimulation of all myeloid lineages hematopoietic progenitor’s proliferation and maturation[3]. Chronic exposure of a resistant clone of an HL60 tumor cell line to ezatiostat resulted in elevated activities of c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase (JNK1) and ERK1/ERK2, and allowed the cells to proliferate under stress conditions that induced high levels of apoptosis in the wild type cells. In vivo, administration of ezatiostat stimulated both lymphocyte production and bone marrow progenitor proliferation[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.89mL 0.38mL 0.19mL |
9.44mL 1.89mL 0.94mL |
18.88mL 3.78mL 1.89mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|