| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
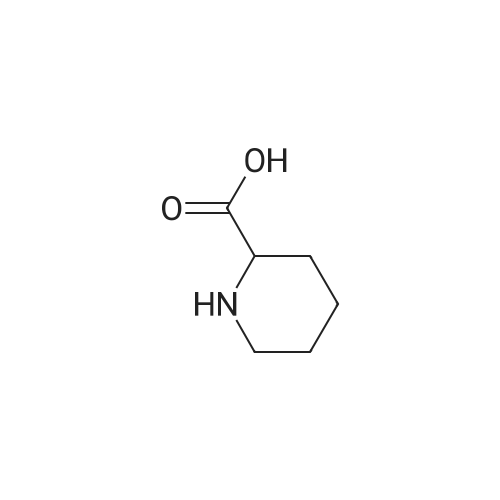
| 描述 | Pipecolic acid, a metabolite of Lysine, is an important precursor of many useful microbial secondary metabolites[1]. Pipecolic acid, a non-proteinogenic amino acid, is a metabolite in lysine metabolism and a key chiral precursor in local anesthesia and macrolide antibiotics[2]. Pipecolic acid (Pip) is an essential component of systemic acquired resistance, priming resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana against (hemi)biotrophic pathogens. Exogenous application of Pip induced resistance in barley against the hemibiotrophic bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas translucens pv. cerealis. Pip induces barley innate immune responses by triggering NO and priming reactive oxygen species accumulation[3]. Moreover, in plants, Pip confers SAR by increasing levels of the free radicals, nitric oxide (NO), and reactive oxygen species (ROS), which act upstream of glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P)[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
7.74mL 1.55mL 0.77mL |
38.71mL 7.74mL 3.87mL |
77.42mL 15.48mL 7.74mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|